The Virchow Triad
Virchow’s triad is a series of 3 changes that occur within the veins and determine the formation of venous thrombi. The condition is also known as venous thromboembolism.
This triad was described by a German pathologist named Rudolf Virchow over 150 years ago. He described, for the first time, the conditions necessary for the venous thrombus to form and spread.
We’ll start by describing the Virchow triad and then explain several definitions that will allow us to understand venous thrombosis and its health risks.
What does the Virchow triad include?
Virchow’s triad includes three changes:
- Abnormalities in blood flow.
- Hypercoagulability: A condition that promotes the formation of clots or venous thrombi.
- Endothelial damage: are lesions within blood vessels.
There are situations known as prothrombotic states that favor the appearance of the triad. Once the factors are brought together, platelets build up like traps that trap neutrophils. Platelets, along with neutrophils, will form venous thrombi and lead to thromboembolism.
What are prothrombotic states?
Prothrombotic states are situations, hereditary or acquired, in which the Virchow triad has a good chance of appearing. They are composed of modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors.
Genetic mutations, when involving clotting factors, can lead to a prothrombotic state. This heritage is difficult or impossible to modify since the risk factor is acquired at the exact moment of conception.
On the other hand, there are systemic diseases that stimulate blood clotting, such as cancer, high blood pressure, kidney disease and chronic venous disease. People with varicose veins and venous insufficiency are particularly susceptible.
Habits and lifestyle are also important in the thrombus equation. Obese people and those who smoke are at high risk. Those who need to travel for long periods by plane, remaining immobile, can stimulate clotting in their legs.
For women, the use of estrogen in hormonal contraceptives deserves special attention. A physician should always assess the risk of thrombosis before recommending such contraception. During pregnancy, pressure from the uterus on the veins that go towards the lower limbs slows down circulation, favoring the Virchow triad.
Other associated situations include:
- Chronic obstructive lung disease.
- Air pollution.
- Lower limb trauma.
- Prolonged immobilization for hospitalizations longer than 48 hours.
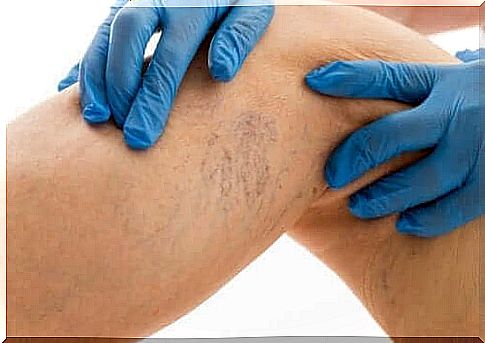
What is venous thromboembolism?
Venous thromboembolism brings together two entities that can cause vascular incapacity and death. In fact, they are the most common cause of preventable death in hospitalized people:
- DVT or deep vein thrombosis
- Pulmonary thromboembolism
Venous thrombi can remain in their place of formation or detach from where they formed to travel through the bloodstream. If detachment occurs, they will be transformed into emboli, which if they reach the heart, pass to the pulmonary circulation.
Lower limb thrombosis is the most common. Causes redness, hypersensitivity to touch, local heat, cramps and pain.
If pulmonary thromboembolism occurs, symptoms are shortness of breath, syncope or fainting, hypotension, and cyanosis (blue skin color). The outcome is deadly without timely and adequate treatment.
How are Virchow triad problems diagnosed?
The most common way to identify deep vein thrombosis is through Doppler ultrasound of the deep venous system. The sonographer examines the presence of blockages in the blood flow or assesses the loss of compression in the veins.
In cases of difficult diagnosis, or in doubtful cases, a computed tomography or nuclear magnetic resonance of the suspected limb will be performed.
For pulmonary thromboembolism, the main method of diagnosis will be pulmonary computed tomography. Sometimes a diagnostic study called pulmonary gammagraphy is required.

Why is Virchow’s triad important?
As we increasingly know about blood clotting and Virchow’s triad, cases related to hospital admissions for thrombi and emboli have decreased. However, an even greater number of deaths from these causes can be avoided.
Maintaining healthy lifestyle habits and caring for our limbs is critical to reducing the risk of hypercoagulation within the bloodstream. Consult a doctor if you are unsure about steps you can take to protect yourself.







