What Is Glucose For?
Glucose is one of the essential molecules for life, as it is the main source of energy for our body’s cells. In other words, it is the nutrient that allows our cells to obtain enough energy to perform all their functions.
It is a form of sugar found freely (as in fruits) and as part of other larger molecules called polysaccharides. The best known polysaccharides are starch and glycogen, found in rice, meat and other foods.
It is very important to know that it is involved in practically every process that is part of our metabolism. In this article, we explain what it is for and what issues are related to it.
What is glucose for?

First, as we’ve already mentioned, glucose is a nutrient acquired through food. During the entire digestion process, it is obtained and used by every cell in our body.
When we eat any food, its nutrients, whether fatty acids, proteins or carbohydrates, pass into the blood and reach the liver. In this organ, complex procedures are performed that end up transforming these nutrients into glucose.
It then passes into the blood and so, through it, it can reach all parts of our body. Cells use this molecule as fuel for energy. They do this through a series of reactions that are the basis of our metabolism.
In this way, glucose allows our cells to nourish themselves and perform all their functions. Thus, it participates in cell reproduction, tissue repair, muscle movement, nerve function, and so on.
What health problems stem from glucose?
Although, as we’ve already mentioned, we can’t live without glucose, there are also glucose-related illnesses. The most important and known is diabetes. It is a disease in which insulin is not produced or there is resistance to it.
Insulin is the substance that allows glucose to pass into cells. So to speak, it is the “key” to this molecule. When our bodies are unable to make or use it, much of the glucose remains in the blood.
This makes cells have less of this molecule. In addition, it can damage many tissues in the body. The most affected are usually the blood vessels, heart and kidneys.
Unfortunately, diabetes is a multifactorial disease that is rapidly increasing in incidence today. This occurs for many factors, such as the sedentary lifestyle and the type of food we eat.
To avoid all the risks that this pathology entails, it is very important to maintain strict blood glucose control. Furthermore, we must be aware of our lifestyle habits and try to change them.
How is glucose measured?
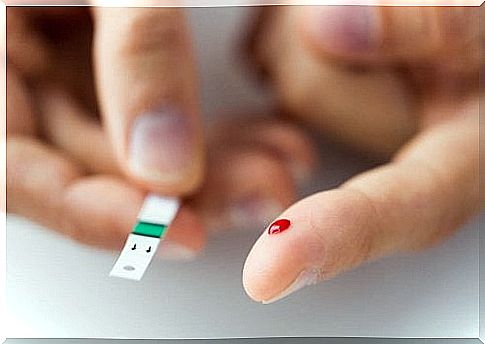
Today there are many methods to control blood glucose levels. It is normal for glucose to be below 100 mg/dl when we are fasting. That is, when it is above these values, it can mean that there is a problem with its passage to the cells.
For the measurement we can use a glucometer. It is a device that, from a drop of blood, provides the result in a few seconds. You just need to make a little prick on your finger. In addition, it is also possible to tell by a blood test or by measuring the glucose that is expelled by the kidneys in the urine.